Microphone Komputer
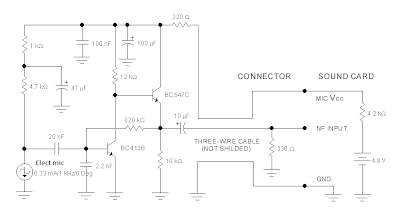
Transistor BC413B operates in common emitter to give a slight boost to the mic signal. This is followed by an emitter follower stage using transistor BC547C. This is necessary as the mic and circuit and battery will be some distance from the sound card, the low output impedance of the circuit and screened cable ensuring a clean signal with minimum noise pickup.
Transistor BC413

Transistor BC547C

The sound card for a PC generally has a microphone input, speaker output and sometimes line inputs and outputs. The mic input is designed for dynamic microphones only in impedance range of 200 to 600 ohms. Lazar has adapted the sound card to use a common electret microphone using this circuit. He has made a composite amplifier using two transistors.
Transistor BC413B operates in common emitter to give a slight boost to the mic signal. This is followed by an emitter follower stage using transistor BC547C. This is necessary as the mic and circuit and battery will be some distance from the sound card, the low output impedance of the circuit and screened cable ensuring a clean signal with minimum noise pickup.
Transistor BC413
- Collector Emitter Voltage VCEO 30 V
- Collector Base Voltage VCBO 45 V
- Emitter Base Voltage VEBO 5.0 V
- Collector Current Continuous IC 100 mA
- Power Dissipation at Ta=25ºC PD 350 Mw Derate Above 25ºC 2.8 mW/ºC
- Power Dissipation at Tc=25ºC PD 1.0 W Derate Above 25ºC 8.0 mW/ºC
- Operating and Storage Junction TJ, Tstg ºC - 55 to +150

Transistor BC547C
- Collector-Base Voltage VCBO (IE = 0) 50 V
- Collector-Emitter Voltage VCEO (IB = 0) 45 V
- Emitter-Base Voltage VEBO (IC = 0) 6 V
- Collector Current IC 100 mA
- Collector Peak Current ICM 200 mA
- Total Dissipation at Ptot TC = 25 oC 500 mW
- Storage Temperature Tstg -65 to 150 oC
- Operating Junction Temperature Tj Max. 150 oC

Tag :
Microphones

0 Komentar untuk "Microphone Komputer"