Transistors operating
Collector current IC of the proportional relationship with the current IB IC = β IB. The greater the current of IB also current IC. Data specification transistor (from factory) in the set maximum value that should not be skipped in the operation. This specification provides limits of transistor operation in the series.
Common Base Configuration
At the bottom of the active region, where the emitter current IE = 0, collector currents flow only from behind the ICO the saturation value is very small (in the micro-ampere), so it can be ignored.
the cut-off is defined as the area where the current IC = 0 A. or indicate : "Regional cut-off occurs when Junction base-collector and base-emitter Junction in reverse bias."
Saturation region is a region where the value of a negative voltage VCB. or indicate: "Region is a region where saturation Junction base-collector and base-emitter Junction in forward bias."
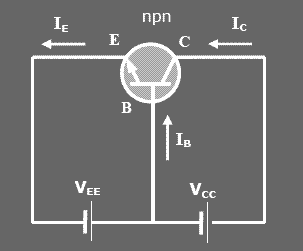
Transistor operating with a bias in both Junction (base-emitter and base-collector). Total current from the emitter terminal is the same as the flow in the collector terminal on the terminal plus cash basis.
- IE = IB + IC
Collector current IC of the proportional relationship with the current IB IC = β IB. The greater the flow of IB also IC flow, seems to have the flow. Data specification transistor (from factory) in the set maximum value that should not be dilampaui in operation. This specification provides limits of transistor operation in the series.
Collector current IC consists of two components, originating from the majority carrier and minority carrier. Flow of minority carriers is called the ICO
- IC = IC majority + ICO minority
Collector current IC of the proportional relationship with the current IB IC = β IB. The greater the current of IB also current IC. Data specification transistor (from factory) in the set maximum value that should not be skipped in the operation. This specification provides limits of transistor operation in the series.
Common Base Configuration
Naming base comes from the common condition where the base used in the joint input and output.
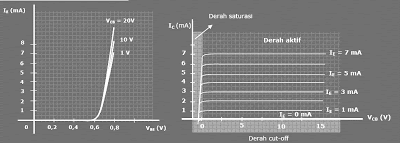
Direction of flow indicated is the direction of conventional flow. Characteristics such as the strengthening of this characteristic is described in kurva input and output characteristics kurva. Characteristics between the input current IE to the input voltage VBE for some value of output voltage VCB. Characteristics of the output current output voltage of IC output for some values VCB IE.

Kurva Karakteristik input & output Common Base Configuration
Characteristics of output has three working areas, namely active, the cut-off and saturation. Active region is a region where the linear case. Specifically stated: "In the active region, Junction base-collector reverse bias while at the Junction in the base-emitter forward bias. "
At the bottom of the active region, where the emitter current IE = 0, collector currents flow only from behind the ICO the saturation value is very small (in the micro-ampere), so it can be ignored.
the cut-off is defined as the area where the current IC = 0 A. or indicate : "Regional cut-off occurs when Junction base-collector and base-emitter Junction in reverse bias."
Saturation region is a region where the value of a negative voltage VCB. or indicate: "Region is a region where saturation Junction base-collector and base-emitter Junction in forward bias."
Characteristics of the input seen that for fixed value of VCB, when the base-emitter voltage (VBE) has increased, flow increased as well as the emitter on the diode. Raising the voltage VCB has a very small impact so that it can be ignored. Model ekivalen input from kurva characteristics are as following picture:
In DC mode, flow-level IC and IE comes from the majority carriers have a relationship:
Tag :
Op-Amp/ Penguat






0 Komentar untuk "Rangkaian Common Base Configuration"